Digital Dosimetry and AI: Shifting from Reactive to Proactive Radiation Safety
Written by
Chris Passmore, CHP, and Mirela Kirr
President and Senior Vice President of Operations & Technical Services
Last Updated: January 6, 2026
Accurate and timely radiation dose tracking is essential for protecting healthcare workers, maintaining compliance, and optimizing procedures. Traditional passive dosimetry methods, such as thermoluminescent dosimeters (TLDs) and optically stimulated luminescent (OSL) dosimeters, are well-established and remain central to many monitoring programs. For directors of radiology (DORs), imaging services leaders, and radiation safety teams, dose tracking is more than a physics function – it directly impacts regulatory readiness, worker safety, staffing stability, and reputation.
This content was originally published in the September/October 2025 issue of Radiology Management, the journal for AHRA, and is being republished with permission. Visit AHRA’s website at ahra.org to learn more.
In today’s hospital environment, where interventional radiology, cardiology, and Theranostic treatments are increasing, gaps in radiation monitoring can lead to employee dissatisfaction with delayed dose reporting, increased liability, and operational delays.
However, evolving clinical workflows, multi-site operations, mobile imaging services, and the increasing use of high-dose modalities are introducing new challenges for radiation safety officers (RSOs) and compliance teams. In these environments, passive-only programs may face limitations related to turnaround times, data granularity, and wearer compliance.
Digital dosimetry, combined with artificial intelligence-powered analysis, offers a complementary approach to enhancing existing programs and supporting proactive exposure management.
Key Takeaways
- Digital dosimetry transforms radiation safety from reactive to proactive by providing near real-time, high-frequency dose data instead of delayed quarterly reports.
- AI-powered analytics enhance decision-making through dose forecasting, anomaly detection, and automated trend analysis that reduce manual review burden.
- Granular dose data improves protection for high-risk and sensitive populations, including interventional staff, traveling clinicians, and declared pregnant workers.
- Timestamped exposure records enable accurate separation of occupational vs. non-occupational dose, supporting regulatory compliance and audit defensibility.
- Digital tools complement (not replace) passive dosimetry, strengthening overall program performance while preserving the legal dose of record.
Benefits of High-Frequency Dose Monitoring
Digital dosimeters record exposure in near real-time, with some models capturing down-to-hourly dose increments. These devices store data locally and transmit it wirelessly via Bluetooth or gateway-enabled communication to a centralized, cloud-based application. This allows individual workers, RSOs, and teams to access and review dose histories without relying on physical dosimeter exchanges or external lab processing.
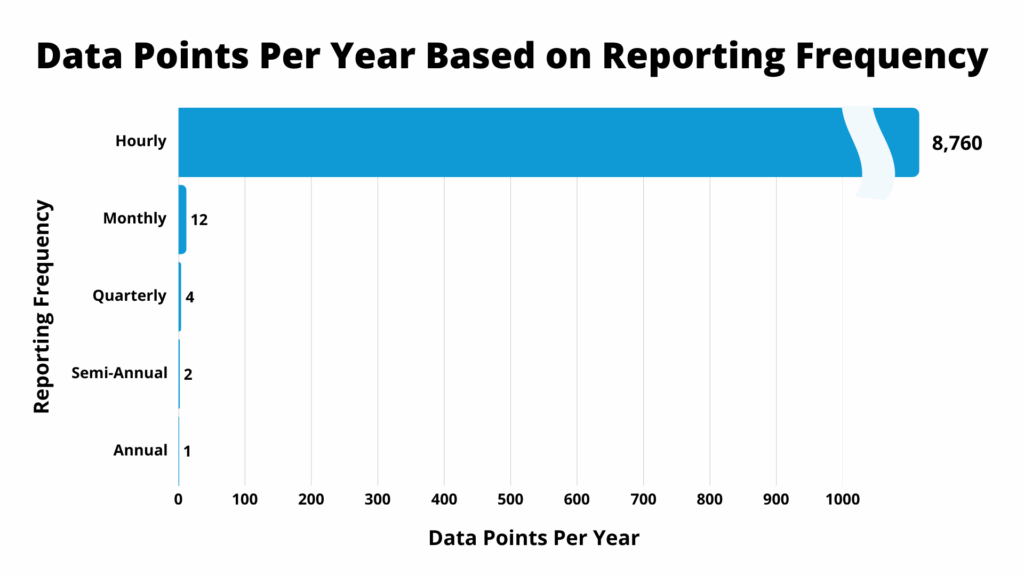
Figure 1. Data Points Per Year Based on Reporting Frequency
Digital dosimetry paired with AI streamlines dose surveillance, identifies anomalies, and delivers predictive insights from 8,760 annual data points per wearer. This enables faster decisions, more accurate reporting, and a shift toward proactive radiation safety management. Source: Radiation Detection Company (RDC)
AI-powered digital dosimetry delivers 8,760 data points per year, vastly outpacing traditional passive dosimetry. High-frequency dose monitoring enables deeper insights for RSOs through granular trend and anomaly detection. In turn, more robust insights can improve surveillance of fetal, high-exposed workers, and personnel at risk of exceeding ALARA Levels.
For imaging departments, this translates to earlier risk identification, faster intervention after dose anomalies, and greater confidence in shielding protocols, procedural rotation policies, and compliance reporting – especially during State and NRC inspections, TJC, or DNV inspections and surveys.
Role of AI in Dose Data Interpretation
Furthermore, AI enhances the utility of digital dosimetry by automating pattern recognition, identifying statistical outliers, and generating predictive insights. These functions allow RSOs to move beyond static reporting into continuous surveillance and rapid-response scenarios.

Key AI capabilities include:
- Threshold forecasting: Predicting when cumulative dose may exceed ALARA or regulatory limits.
- Pattern identification: Detecting exposure trends linked to specific procedures, workers, or locations.
- Dose anomaly alerts: Flagging readings that fall outside normal operational parameters.
- Missing dose estimation: Providing risk-adjusted dose reconstructions in cases of lost or damaged dosimeters.
These tools reduce the burden of manual data review and support more confident decision-making in fast-paced clinical environments.
For department leaders, this means reduced reliance on post-hoc incident reviews and a greater ability to take preemptive safety actions that align with system-level goals like zero-harm initiatives and centralized program management.
Case Applications and Operational Use
In the section below, we explore three case studies that illustrate how digital dosimetry and AI can help resolve data gaps and overcome challenges of traditional passive dosimeters in various settings.

Radiation Detection Company’s digital dosimeter, NetDose™, received the 2025 AHRA Innovation Award, presented by the Association for Medical Imaging Management (AHRA).
Case 1: Cardiologist Exposure Forecasting
A cardiologist at a large hospital averaged 4-6 procedures per day. A digital dosimeter showed hour-by-hour exposure – the dose reached 562 mrem (5.62 mSv) by Day 30, and 829 mrem (8.29 mSv) by Day 45.
AI anticipated the exposure rate and projected that the cardiologist would have reached the ALARA I threshold within 68 days and the federal limit nine months into the year. Without a digital dosimeter, the cardiologist would have relied on traditional passive quarterly reporting, creating a data void and putting him at risk.
This prediction enabled early procedural adjustments and engineering controls to address and reduce cumulative exposure. Traditional quarterly passive dosimetry reporting would not have captured this trend in time.
Discover how digital dosimetry can assist hospital staff in preventing delayed radiation dose data and taking corrective actions to ensure radiation safety and compliance: The Hidden Risks of Delayed Radiation Dose Feedback in Hospitals.
Case 2: Dose Delays and Pregnancy Declarations

Employees may not declare their pregnancy until weeks or even months into knowing that they're pregnant. This delay forces the RSO to make the past dose exposure based on incomplete data.
Pregnant employees wear dosimeters for a month and have to wait another 20 days for processing and the results to arrive; critical dose information is already four to six weeks old before they even reach the decision maker and the pregnant employee working in the field of radiation.
With digital dosimetry, RSOs can immediately access cumulative and time-specific dose data and make timely decisions regarding task reassignment. The delayed latency of traditional dosimeter processing creates undue stress for the worker and could potentially cause unknown risks to the pregnancy/fetus.
Case 3: Non-Occupational Exposure Detection
A radiologic technologist student triggered elevated exposure levels over multiple days. Digital dose pattern analysis showed a dose pattern occurring exclusively in the evenings, spread over multiple days, with 6 out of 7 events occurring on the weekend. The student had conducted an experiment: 95% of the student’s total 440 mrem dose was non-occupational.
The investigation confirmed that the exposures were non-occupational and unrelated to supervised activities. Without timestamped data, this differentiation would have been significantly more difficult.
Proactive radiation safety starts with real-time data.
See how NetDose™ and MyRadCare Insights™ translate digital dose data into actionable intelligence.
Case 4: Traveling Healthcare Workers and TSA Airport Screening
Healthcare professionals who travel frequently between clinical sites may encounter unexpected dose contributions from airport security processes. In one documented case, a worker accrued a total exposure of 310 mrem over a two-month period. Upon closer examination, only 5 mrem was attributed to occupational sources. The remaining 305 mrem was linked to repeated passage of the dosimeter through TSA CT scanners at airport checkpoints.
Digital dosimetry data, recorded in hourly increments, enabled clear separation of occupational and non-occupational exposure by aligning timestamped dose events with the worker’s travel schedule. A pattern emerged across 16 airports, with scanner-related dose ranging from 21 to 95 mrem per trip, and an average of 63 ± 20 mrem per encounter.
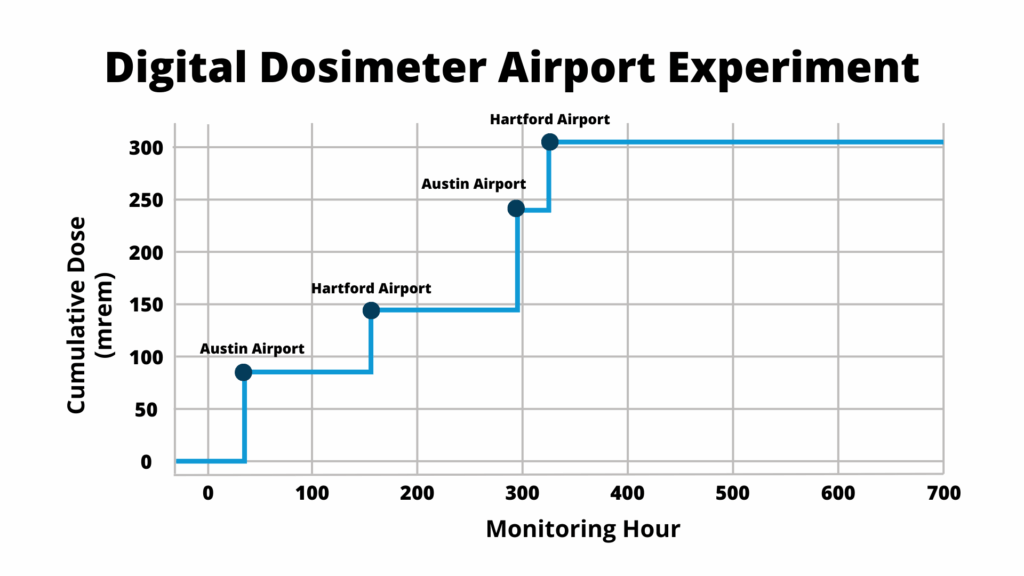
Figure 2. Recreated Airport Experiment
RDC President, Chris Passmore, CHP, conducted a personal experiment while traveling to measure the cumulative radiation dose by monitoring hour. 305 mrem came exclusively from CT scanner exposure at airport checkpoints – leaving just 5 mrem as actual occupational dose. Source: Optimizing Dose Monitoring for Traveling Employees
This case underscores a key challenge in maintaining regulatory compliance under NRC 10 CFR § 20.1003, which requires accurate distinction between occupational and incidental exposures. Without granular digital data, the individual’s total exposure may have triggered unnecessary internal reviews or misrepresented program performance.
Digital dosimetry, supported by AI classification tools, provided the contextual evidence needed to adjust the dose of record and maintain reporting accuracy.
Case 5: Dose Reconstruction for Missing or Damaged Dosimeters
In large dosimetry programs, approximately 8% of dosimeters issued are lost, and 0.9% are damaged or exhibit abnormal response; out of every 100 dosimeters issued, approximately nine will require a dose reconstruction to provide an estimate of the worker’s radiation exposure.
In one instance, a control room worker entered a restricted area without wearing their assigned dosimeter. Although the individual self-reported the lapse, no recorded data was available to quantify the exposure. Using digital dosimetry from peer workers assigned to similar roles and shifts, combined with AI modeling of historical dose trends, the RSO was able to produce a risk-adjusted dose estimate based on exposure time, location, and task type.
AI can validate the reconstructed dose through trend comparison and deviation analysis against cohort data. This approach ensures regulatory compliance while minimizing unnecessary administrative burden or exposure assumptions.
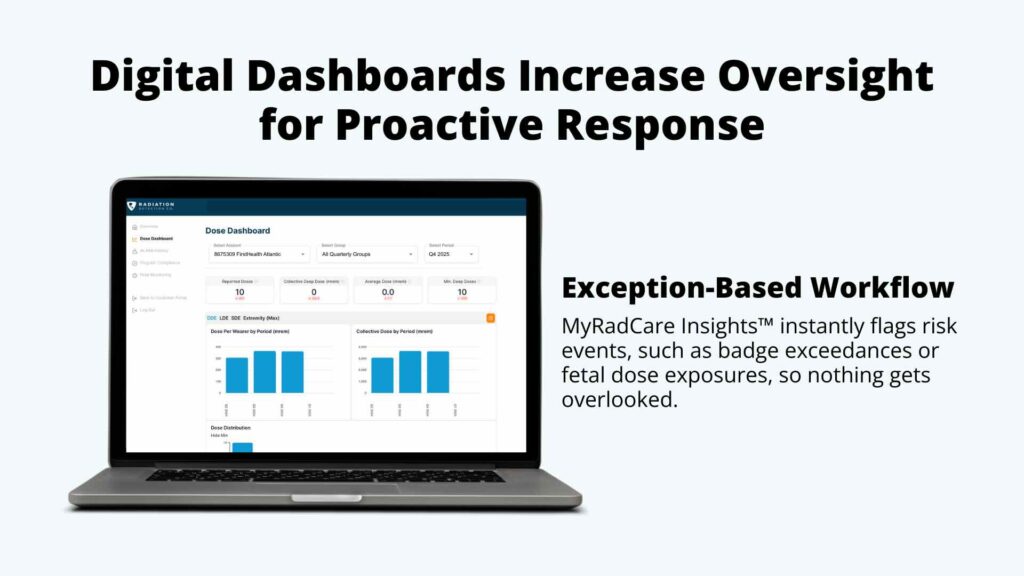
Digital dosimetry platforms, augmented with AI-driven imputation tools, enable RSOs to reconstruct dose with greater confidence and contextual accuracy, especially in time-sensitive scenarios. This not only enhances program reliability but also improves documentation consistency for audits and inspections.
AI-Driven Advantages: Benefits for Compliance and Program Management
Organizations implementing digital dosimetry and AI analytics have reported the following benefits:
- Faster incident response: Real-time data allows near-immediate assessment and proactive corrective action.
- Improved dose granularity: Hourly intervals support more accurate dose reports.
- Administrative efficiency: Eliminates dosimeter exchange logistics, late returns, and distribution bottlenecks.
- Enhanced audit readiness: Cloud-based access to historical dose records simplifies inspection preparation.
Imaging directors can also streamline coordination across modalities (such as CT, IR, and nuclear medicine), ensuring dose metrics are consistent across facilities and that risk management teams have the documentation they need in minutes, not weeks.
Digital platforms also enable cross-site standardization by providing centralized dashboards and customizable alert thresholds. This facilitates consistent program oversight for integrated delivery networks (IDNs) or systems with multiple imaging locations.
At Radiation Detection Company (RDC), we leverage real-time, exception-based reporting to help organizations improve compliance, reduce badge loss, and save time. Explore our smart radiation safety analytics platform: MyRadCare Insights™.
What to Consider: Integrating Digital Dosimetry into a Multi-Modal Strategy
Rather than replacing traditional passive dosimetry, teams can employ digital solutions selectively in high-risk environments and instances that would benefit from more granular readings.
Directors of radiology may consider starting with a phased approach – prioritizing digital dosimetry for high-use fluoroscopy, cardiac imaging, or mobile teams, while continuing passive programs for standard departments where dose variability is low. This balances innovation with cost-effective operations.
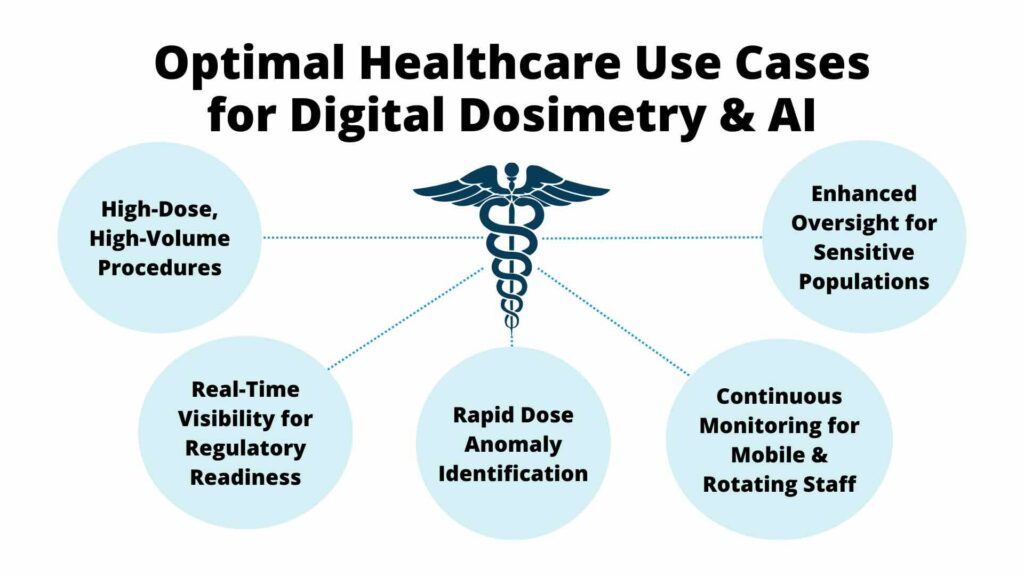
Digital dosimetry can be especially beneficial in scenarios involving:
- High-utilization environments like fluoroscopy or interventional radiology departments
- Instances involving dose anomalies or uncertainties in exposure records
- Teams with unique monitoring needs, including declared pregnant workers, mobile staff, or rotating shift workers
This selective deployment model allows organizations to gain actionable insights in high-risk or high-variability scenarios while maintaining passive dosimeters for routine program documentation.
As a general guideline, digital dosimetry and AI are best suited for environments where:
- High-dose modalities (for example, interventional cardiology, PET/CT, mobile fluoroscopy) are frequently used
- Staff are difficult to monitor using traditional dosimeter distribution/return models
- Previous compliance issues, dose anomalies, or data latency have been observed
- Regulatory pressure for real-time monitoring and response is increasing
In these contexts, adding digital and AI capabilities can strengthen overall program performance without displacing passive systems that fulfill the legal dose of record requirements.
Final Thoughts: The Future of Healthcare Dosimetry
Digital dosimetry and AI provide RSOs, physicists, and safety committees with more precise, timely, and actionable information. They support a shift in program posture from retrospective reporting to predictive risk mitigation.
For imaging department leaders and healthcare executives, this shift supports strategic priorities such as quality assurance, workforce safety, and regulatory excellence. By equipping teams with real-time exposure data, healthcare systems can strengthen their radiation safety culture while reducing the administrative and clinical risks associated with delayed or incomplete data.
By integrating these technologies into targeted areas of their operations, healthcare organizations can better protect staff, streamline program administration, and respond more effectively to regulatory requirements. When applied strategically, digital tools enhance, not replace, the foundational value of passive dosimetry systems.
Want to learn more about how digital dosimetry and AI can benefit your organization? Call 800.250.3314 or complete our contact form to get answers and step into the future of healthcare dosimetry.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does digital dosimetry replace traditional passive dosimeters?
No. Digital dosimetry is designed to complement passive dosimeters, not replace them. Passive dosimeters remain the legal dose of record, while digital tools provide high-frequency data that enhance monitoring, investigation, and proactive risk management.
How does AI improve radiation dose monitoring?
AI automates pattern recognition, predicts when dose thresholds may be exceeded, flags anomalies, and assists with dose reconstruction when data is missing, allowing RSOs to act sooner and with greater confidence.
Is digital dosimetry useful for declared pregnant workers?
Yes. Digital dosimetry provides immediate access to cumulative and time-specific dose data, reducing uncertainty and stress caused by delayed passive dosimeter reports and enabling timely work adjustments when needed.
Can digital dosimetry distinguish occupational from non-occupational exposure?
Yes. Timestamped, high-resolution dose data allows RSOs to correlate exposure events with work schedules, travel, or other activities, supporting accurate classification and regulatory compliance.
Which departments benefit most from digital dosimetry?
Digital dosimetry is especially valuable in high-dose or high-variability environments such as interventional radiology, cardiology, mobile imaging, PET/CT, and for staff who travel frequently or rotate across sites.
Want real-time visibility into radiation exposure?
Discover how NetDose™ digital dosimeter and MyRadCare Insights™ help healthcare teams move from delayed reporting to proactive radiation safety management.
Learn more about digital dosimetry solutions →